
The real reason your content is not engaging online
Are your social media or content marketing efforts under performing? Before you spend any more time tweaking your content strategy and onlin... Read more
13 May, 2025Making sense of international marketing and brand strategy in the information age

Are your social media or content marketing efforts under performing? Before you spend any more time tweaking your content strategy and onlin... Read more
13 May, 2025
What are the opportunities and challenges facing brands who wish to market themselves internationally? This was the focus of "Amerikadagen."... Read more
6 May, 2025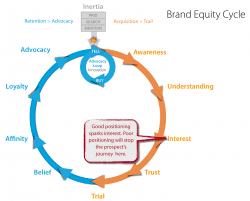
Few things will help your brand build an engaging online audience faster than a strong position. Your brand’s position is an early gat... Read more
29 April, 2025
What does a digital marketing strategist do? In fact, if such specialists work in a digital marketing agency, a better question might be, wh... Read more
28 April, 2025
Marketing is a balancing act between a slew of conflicting forces for growth. Here's a simple model to help the marketing department establi... Read more
9 April, 2025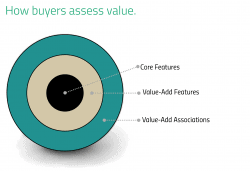
If you work for a mid-sized company that is looking for growth, we suggest rethinking the business paradigm your business operates under.... Read more
26 March, 2025
Is it really possible to define a brand position that works globally? When Jack Trout and Al Ries penned the marketing classic, "Position... Read more
25 March, 2025When people think about cross-cultural marketing blunders they usually think of the funny translation gaffs. There are dozens of examples. ... Read more
4 March, 2025
The second in a three-part series on best practices to focus your brand's offer and communication.... Read more
21 February, 2025
In my previous post on Growth Strategy, I mentioned the various stages of digital evolution businesses have been going through. A decade ago... Read more
18 February, 2025