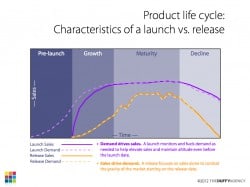
How to bring your product launches to new heights
APPLE SHOWS US HOW IT'S DONE WITH THE iPHONE 5 It may be apple season (with a small "a") in many parts of the Northern Hemisphere, but gl... Read more
14 July, 2023Making sense of international marketing and brand strategy in the information age

APPLE SHOWS US HOW IT'S DONE WITH THE iPHONE 5 It may be apple season (with a small "a") in many parts of the Northern Hemisphere, but gl... Read more
14 July, 2023
In my previous post on Growth Strategy, I mentioned the various stages of digital evolution businesses have been going through. A decade ago... Read more
12 July, 2023When people think about cross-cultural marketing blunders they usually think of the funny translation gaffs. There are dozens of examples. ... Read more
10 July, 2023
Before you even think about online networking for your brand, I suggest the following exercise. First, take your shoes off. Close the blinds... Read more
5 July, 2023
How to create your own marketing micro-profession Before getting involved in advertising, I had planned on attending medical school. A lo... Read more
3 July, 2023
The added value that neuromarketing brings to market research is that it starts where traditional research methods end – in the consumer b... Read more
7 May, 2023
Is it really possible to define a brand position that works globally? When Jack Trout and Al Ries penned the marketing classic, "Position... Read more
14 April, 2023
Marketing is a balancing act between a slew of conflicting forces for growth. Here's a simple model to help the marketing department establi... Read more
9 April, 2023
What are the opportunities and challenges facing brands who wish to market themselves internationally? This was the focus of "Amerikadagen."... Read more
7 April, 2023
Q&A with Sean Duffy on the role of the brand strategist in the internet era. ... Read more
31 March, 2023